Low Ovarian Reserve
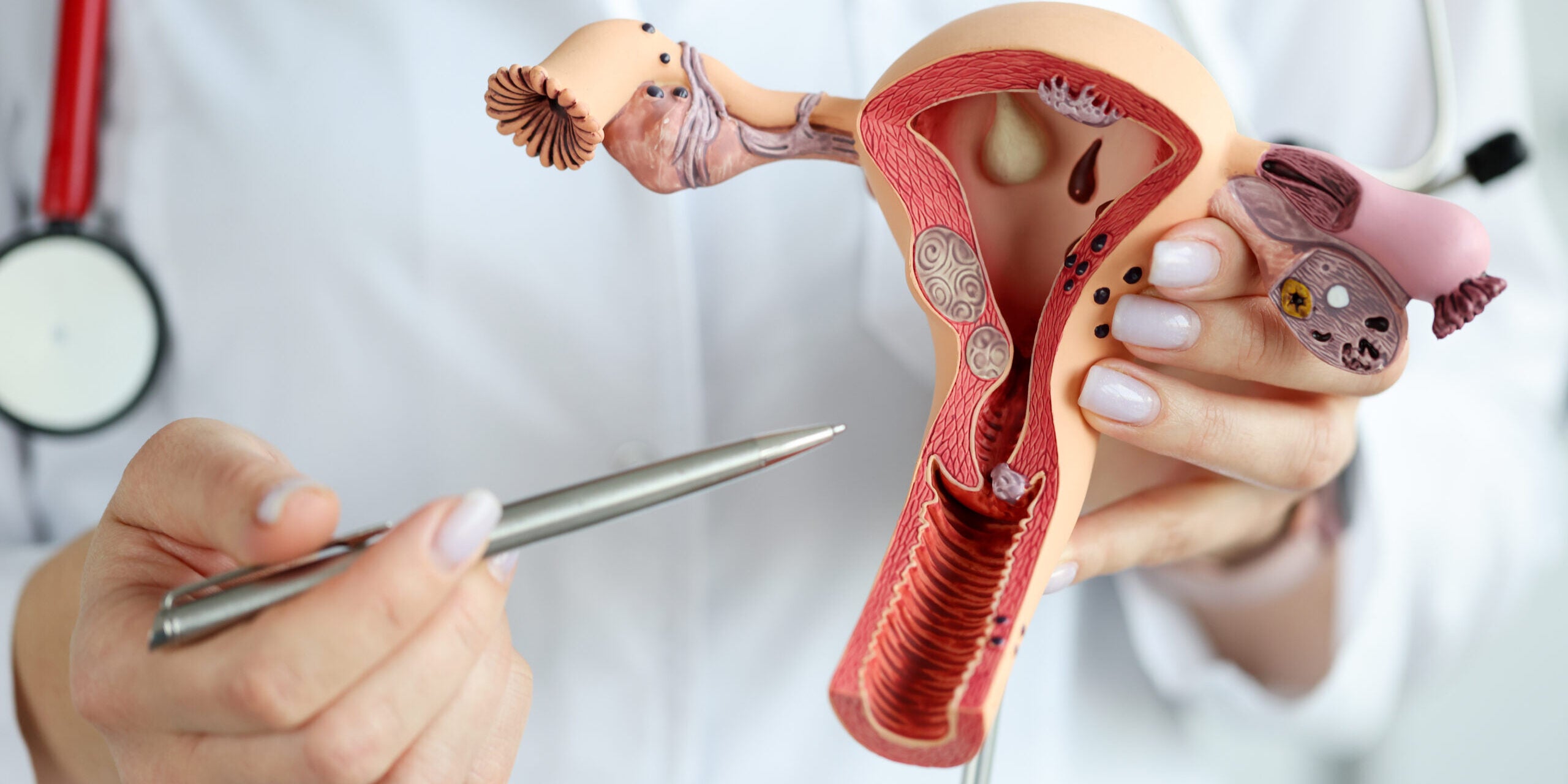
Fertility normally declines with age like all functions of the human body. In women, it can be observed from about the age of 30, becoming more pronounced during the 40s. The human ovary contains a certain number of follicles established before birth that decrease with increasing age and culminate in menopause. The ovarian reserve represents the number and quality of the remaining oocytes.
It is important, for all women who are of childbearing age, to know their ovarian reserve if they want to have children; according to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, it is difficult to predict the rate of reproductive decline in each woman. However, knowing your ovarian reserve will allow you to make important decisions regarding your fertility.

The ovarian reserve represents the number and quality of the remaining oocytes. (Image from Freepik )
What is low ovarian reserve?
Low ovarian reserve or in English, diminished ovarian reserve (DOR) is a problem that affects between 9% and 24% of patients who undergo In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) treatments.
It is a condition in which the ovary loses its normal reproductive potential, compromising fertility. The term represents women of reproductive age who have regular menses and whose response to ovarian stimulation or fertility is reduced compared to women of the same age. Low ovarian reserve is distinct from menopause or premature ovarian failure.
What are the causes?
This commonly occurs as a result of normal aging of the ovaries. However, there are other factors that can also contribute:
- Tubal diseases
- endometriosis
- Previous ovarian surgery
- Chemotherapy
- radiation therapy
- Smoke
- infections
- autoimmune disorders
- Genetic abnormalities such as fragile X syndrome
What are the symptoms?
Unfortunately, most women have no symptoms when suffering from low ovarian reserve. As the condition progresses over time, women may notice a shortening of their menstrual cycle (for example, 28-day cycles reduced to 24 days). Once menopause is imminent, women may notice signs of low estrogen levels, such as hot flashes, trouble sleeping, intermittent menstrual periods, and vaginal dryness.

Unfortunately, most women have no symptoms when suffering from low ovarian reserve. (Image from Freepik )
How is low ovarian reserve diagnosed?
There are several ways to assess the functional reserve of the ovary, the most frequent are vaginal ultrasound and the test of the anti-mullerian hormone which is done in a blood test.
It is important to note that while these tests are important in diagnosing it, no test is absolutely definitive when it comes to determining whether or not you can get pregnant.

Ovarian reserve is frequently assessed with vaginal ultrasonography and anti-Müllerian hormone testing. (Image from Freepik )
Your doctor may recommend a transvaginal ultrasound early in your cycle. This is to measure the number of antral follicles (between 2 and 10 millimeters) in both ovaries. Follicles are small sacs inside the ovaries that are filled with fluid and each contain one egg. The follicle count lets your doctor know how many eggs are available.
The anti-mullerian hormone or AMH test is performed with a simple blood test. Its levels are related to the number of eggs available for fertilization.
Is there any treatment?
Although at this time there is no specific treatment for low ovarian reserve or to counteract the normal aging of the ovaries, specialists can evaluate each case individually and recommend various treatment options to preserve fertility or help achieve a pregnancy.
Once your doctor diagnoses decreased ovarian reserve, he or she may suggest saving eggs for a future pregnancy if you don't want to get pregnant right away. If you try to get pregnant depending on your age and the results of your ovarian reserve, the doctor will give you his recommendations.
The treatments of Assisted reproduction They are frequently recommended to women with this condition, beginning with ovarian stimulation through the use of hormones or medications to achieve the maximum number of oocytes.

Assisted reproduction treatments are frequently recommended for women with low ovarian reserve. (Image from Freepik )
What can I do to improve my ovarian reserve?
As we mentioned before, the ovarian reserve cannot be changed, but the quality of your eggs can. Getting a better quality can increase your chances of getting pregnant. Using the supplements and vitamins correct, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, staying away from the toxic substances that may be affecting your fertility you will be able to improve your fertility .
Facing a diagnosis of low ovarian reserve can be frightening and disconcerting at the same time. It may have taken you by surprise and you may not feel ready to face it, but it is important to remember that you have options, that with advances in science and technology technology the results of assisted reproduction treatments are increasingly promising and that overcome your fears and face infertility it's possible.
0 comments



